Social Science (213)
Tutor Marked Assignment
20% Marks Of Theory
1. Answer any one the following question in about 40-60 words.
(b) Write about the life and duties of serfs under the feudal system.
Answer: Serfs were peasants who were tied to the land they worked on under the feudal system. They were not slaves but could not leave their land without their lord's permission. Their duties included farming, maintaining the lord's estate, and providing military service. In return, the lord offered them protection and a place to live. Serfs often lived in harsh conditions and had limited rights.
2. Answer any one the following question in about 40-60 words.
(a) Evaluate the major challenges faced by Indian Agriculture.
Answer: Indian agriculture faces several major challenges, including:
Land fragmentation: Small landholdings limit productivity and access to resources.
Lack of irrigation: Dependence on rainfall makes agriculture vulnerable to droughts.
Outdated farming practices: Traditional methods hinder efficiency and yield.
Soil degradation: Overuse and lack of proper management lead to soil erosion and nutrient depletion.
Climate change: Extreme weather events and rising temperatures impact crop production
3. Answer any one the following question in about 40-60 words.
(b) Analyze the functions of Municipal Council.
Answer: Municipal Councils are local governing bodies responsible for providing essential services to their residents. Their primary functions include:
- Urban planning: Developing and implementing plans for land use, infrastructure, and development.
- Public services: Providing essential services like water supply, sanitation, waste management, and street maintenance.
- Property tax: Collecting property taxes to fund municipal operations.
- Regulation: Enforcing building codes, zoning regulations, and other local laws.
- Community development: Promoting social and economic development through programs and initiatives.
4. Answer any one the following question in about 100-150 words.
(a) In what ways has India’s federal structure evolved to accommodate the country’s socio-political diversity?
Answer: India's federal structure has evolved significantly to accommodate its socio-political diversity. Initially, the Constitution established a strong enter with limited powers for the states. However, over time, several amendments have been made to decentralize power and provide greater autonomy to the states.
One of the most significant changes was the introduction of the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments, which established Panchayati Raj institutions and urban local bodies, respectively. These institutions have empowered local communities to participate in governance and decision-making processes.
Furthermore, the Constitution provides for linguistic states, recognizing the importance of regional identities and languages. This has helped to address the concerns of various linguistic groups and promote regional development. Additionally, the establishment of autonomous regions like Jammu and Kashmir and the North-East has provided special status to certain areas with unique cultural, linguistic, or historical identities.
While India's federal structure has evolved to accommodate its diversity, challenges remain. Issues such as inter-state disputes, regional imbalances, and the need for further decentralization continue to be addressed. However, the country's federal framework has proven to be a resilient and adaptable mechanism for managing its diverse socio-political landscape.
5. Answer any one the following question in about 100-150 words.
(a) Evaluate the impacts of linguistic diversity on national integration of India.
Answer: Linguistic Diversity and National Integration in India:
India's linguistic diversity, with over 22 official languages and numerous dialects, has been a defining feature of its national identity. While it poses certain challenges, it also plays a crucial role in promoting national integration.
On the one hand, linguistic diversity can create divisions and hinder communication. Differences in language can lead to misunderstandings, cultural biases, and even conflicts. This is particularly evident in areas with significant linguistic minorities, where language-based discrimination and marginalization can occur.
On the other hand, linguistic diversity can also be a source of strength and unity. India's rich linguistic heritage is a reflection of its cultural diversity, which has contributed to its unique identity. By recognizing and celebrating the diversity of languages, India can foster a sense of belonging and inclusivity among its citizens.
Moreover, linguistic diversity can promote cultural exchange and understanding. When people from different linguistic backgrounds interact and learn from each other, it can break down stereotypes and foster a sense of empathy. This can lead to greater social cohesion and national integration.
To fully harness the benefits of linguistic diversity, India must adopt inclusive language policies and promote multilingualism. This can be achieved through education, media, and government initiatives that support the use of all official languages. Additionally, efforts should be made to address language-based discrimination and promote linguistic equality.
Conclusion:
while linguistic diversity presents challenges for national integration in India, it can also be a powerful force for unity and cultural exchange. By embracing its linguistic diversity and promoting multilingualism, India can build a more inclusive and cohesive nation.
6. Prepare any one project out of the given options:
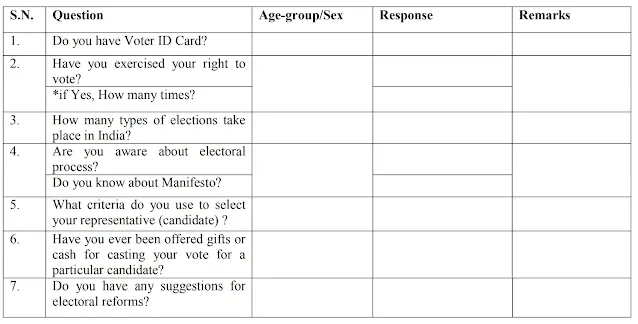
(a) To assess the electoral literacy, conduct a survey around your household. Ask the Following questions from the given survey questionnaire to 20 peoples who are 18 years Old or above and write their responses. Analyze the collected responses and draw your Conclusions.
Answer: Survey Responses
Analysis and Conclusions
Based on the survey responses, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- Most respondents are aware of their voting rights and have exercised them.
- Awareness about different types of elections and the electoral process varies. Many respondents were familiar with general and state elections but lacked knowledge about other types.
- Most respondents prioritize personal qualities and qualifications when selecting candidates. Party affiliation was less important for many.
- Bribery is a concern. While most respondents reported not being offered bribes, it remains a significant issue in Indian elections.
- Respondents suggested electoral reforms to improve voter education and combat corruption.
Overall, the survey indicates a moderate level of electoral literacy among the respondents. While most are aware of their voting rights and have participated in elections, there is room for improvement in understanding the electoral process and its nuances.
Further research and analysis could be conducted to gain a more comprehensive understanding of electoral literacy in the region and identify specific areas for intervention.

%20EM%20Solved%20TMA%202024-25.webp)